Are you into conversational analysis?
Do you have millions of call recordings that you like to range based on audio quality?
Sevana PVQA is the tool that can analyze hours of recorded audio in a couple of minutes.
Request a call with our team to learn more about call recordings quality analysis and other related technologies for audio quality assessment.
Being a multipurpose tool for voice quality analysis PVQA Server can be the core of a quality analysis and monitoring system to detect and investigate QoE and QoS related issues. PVQA Server combines the force of audio waveform analysis using PVQA technology with continuous network monitoring:
🔎Real-time call quality monitoring
🔎Proactive maintenance based on non-intrusive waveform analysis
🔎Monitoring network and media quality simultaneously
🔎Matching network metrics (RTT, jitter, latency, packet loss) with payload metrics (noise, clipping, dead air, echo etc)
Voice quality is the term used to describe the clarity of your voice. It’s more than just the sound of your voice—it also includes things like background noise and interference, which can have an adverse effect on how well your voice is heard. This makes passive voice quality testing and analysis and important part of modern communications.
Sevana AQuA and PVQA libraries collect all the data related to impairments that may affect voice quality in real-time providing immediate alerting and storage of all metrics related to call audio degradation. Audio impairments one can map on network parameters (jitter, packet loss, RTT delay) that will form patterns related to certain routes, destinations, originations. Every call analyzed by the system creates data that one can study using bigdata analysis tools to predict network behavior and call quality.
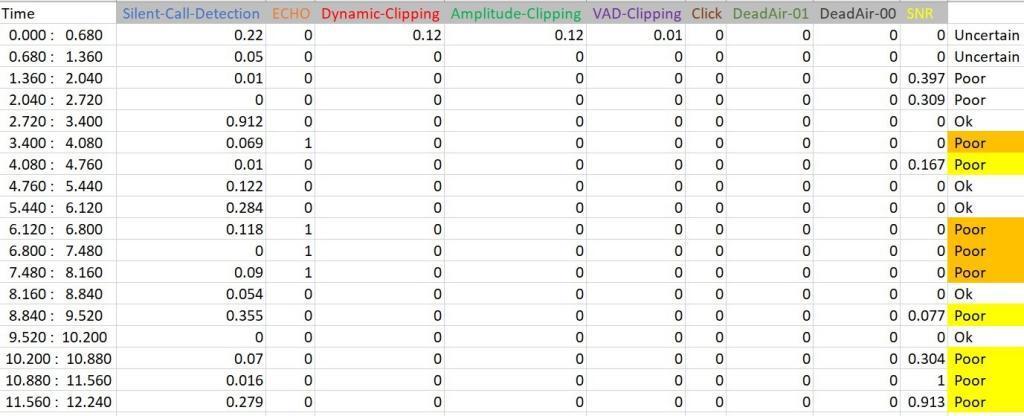
Silent Call – one leg of the voice call has no speech
Echo – this is typically due to a blockage or mismatch, which results in the signals bouncing back from where they came. Additionally, the presence of echo effect in packet switched networks can be traced back to the functionality of the line. Where standard lines function with a delay of 10 milliseconds, packet switched networks can have up to 400 milliseconds of delay. As a result, the echo effect is much more noticeable.
Amplitude clipping – is typically a result of a misconfigured voice gateway on the voice path.
Dynamic clipping – notifies about possible clipping happening in another network as the audio waveform looks like amplitude clipping, however, it is not present at the moment.
VAD clipping – this impairment detects incorrect work of Voice Activity Detector (VAD). Detector finds edges of active and inactive fragments of the signal considering VAD worked too late (in the beginning of the speech) or too early (in the end of the speech).
Click – is a single energy spike in the spectrum of the audio, which may happen for different reasons.
DeadAir-01 – is a zero-signal level inside speech, a gap in speech that may be caused by different reasons.
DeadAir-00 – is a constant signal level inside speech and may have positive and negative value.
SNR – this means that noise level present in the call affects human perception and disturbs the caller.
Within impairments analysis one can not only detect impairments that degraded voice quality in real-time, but in case of post call analysis pinpoint actual time period when certain impairment took place (as it is specified on the picture, Poor intervals are marked with the same color the impairment detectors that triggered the problem, e.g. Echo)
Further more, big data analysis of reports generated by PVQA help to identify impairment patterns specific for certain problems in the networks, e.g.
Click + DeadAir-01 – high probability that packet loss affected the call audio
Click + VAD clipping – possible packet loss
Contact us to have full demo on PVQA analysis or PVQA Server functionality.